
A Glossary of Estate Planning Terms
This is a glossary of some of the estate planning terms used in MSU Extension Estate Planning MontGuides. Keep this glossary close in case you come across an unfamiliar term when you read the fact sheets.
Last Updated: 09/21by Marsha A. Goetting, Ph.D., CFP®, CFCS, Extension Family Economics Specialist, Montana State University-Bozeman
Administrator: Formerly used for a person named in a will to carry out settlement of the estate. Under the Montana Uniform Probate Code, the term is now personal representative.
Alternate Valuation Date: A date exactly six months following the decedent’s date of death that the personal representative may choose to revalue for estate tax purposes, all assets held by the estate.
Ancillary Probate: If decedent had real property in another state probate is required in that state.
Annual Exclusion: The amount of $15,000 that can be given to any individual or any number of individuals gift tax free. A husband and wife together can give $30,000 to each person (2021).
Annuity: The periodic payment of a definite sum of money, with such payments to continue for life or for a definite number of years.
Assets: All types of property which can be made available for the payment of debts.
Attorney: Another name for a lawyer.
Beneficiary: A person (or institution) who derives benefit from the creation of a trust, proceeds of insurance policy, IRA or other retirement plan, or property designated by a will.
Beneficiary Deed: One in which an owner conveys an interest in Montana real property to grantee beneficiary upon the owners' death prior to October 1, 2019.
Closely-Held Business: A business organization in which the ownership is held by a limited number of people often with the same family rather than owned by the public at large.
Codicil: A supplement, amendment, or addition to a will executed with all the formalities of the will itself. It may explain, modify, add to, subtract from, qualify, alter, or revoke provisions in a will.
Common Disaster Clause: A statement in a will telling how property is to be distributed if would-be devisees die from the same accident.
Conservator: A person who is appointed by a court to manage the estate of a protected person who, because of age, intellect, or health, is incapable of managing his or her own affairs.
Consideration: Something which has value, such as real or personal property or a promise given in exchange for another promise.
Contingency: The possibility of coming to pass; an event that may occur.
Corpus: Trust property; the principal sum as distinguished from interest or income.
Custodial Account: A way to gift during life, bequests with a will, or distributions from a trust for the benefit of a child who is under 21.
Death Taxes: Taxes due by reason of death of an individual.
Decedent: A deceased person.
Deed: A legal instrument used to transfer title to real property in the eyes of the law.
Devise: When used as a noun, real or personal property given to another by will. When used as a verb, to dispose of real or personal property by will.
Devisee: Any person designated in a will to receive real or personal property.
Disposition Direction: The Montana Right of Disposition Act allows disposition directions in four formats: 1) prepaid funeral contract; 2) written disposition direction; 3) signed affidavit; and 4) videotaped disposition direction.
Domicile: A person's true, fixed, and permanent home and place of habitation.
Donee: One who receives a gift.
Donor: One who makes a gift.
Durable Power of Attorney: Allows the grantor of the power of attorney to survive any disability the grantor could suffer.
Escheats: When a decedent’s property goes to the state because of lack of heirs.
Estate Tax (Federal): Taxes assessed by the federal government upon a decedent’s transfer of property. In 2021, a single person who has less than $11.7 million does not pay a Federal Estate Tax; a married couple can pass $23.4 million without a estate tax. The amount is adjusted annually for inflation.
Exempt Property: Property not exceeding $15,000 in value in excess of any security interests in household furniture, automobiles, furnishings, appliances and personal effects to which a surviving spouse is entitled from the estate. This property is protected from creditors and devisee claims (Montana law).
Family Allowance: The surviving spouse and minor children are entitled to a reasonable family allowance in cash from the estate for their maintenance during the period of probate administration. The personal representative may determine the family allowance in a lump sum not exceeding $27,000, or periodic installments not exceeding $2,250 per month for one year (Montana law).
Fiduciary: Includes personal representative, guardian, conservator and trustee.
Formal Probate Proceedings: Those conducted before a judge with notice to interested persons for probate of a will or appointment of a personal representative.
Grantee Beneficiary: Party to whom an owner grants an interest in Montana real property described on a beneficiary deed.
Gross Estate: For federal estate tax purposes, the total value of all property – real or personal, tangible or intangible – that a decedent had owned or had control over at the time of death.
Guardian: A person legally empowered and charged with the duty of taking care of another who, because of age, intellect, or health, is incapable of managing his or her own affairs. The guardian manages the person. A conservator manages the property of a minor or incapacitated person. A person can be appointed both guardian and conservator.
Heirs: Those persons who are entitled under the statutes of intestate succession to the property of a decedent.
Holographic Will: A will in which the signature and material provisions are in the handwriting of the testator. A holographic will does not need to be witnessed.
Homestead Allowance: A surviving spouse of a decedent who was a resident of Montana is entitled to a homestead allowance of $22,500.
Informal Probate Proceedings: Those conducted without notice to interested persons by the clerk of the court for probate of a will or appointment of a personal representative.
Inherit: To receive property from a deceased person.
Inter Vivos Trust: Legal name for a living trust. The trust is set up by the grantor during his or her lifetime.
Intestate: A term used when a person dies without leaving a valid will.
Irrevocable: Trust in which the trustor (maker of the trust) has, by the terms of the trust agreement, specifically given up the power to alter, amend, or terminate the trust either entirely or in part. In Montana, unless a trust is expressly made irrevocable by the document that establishes it, it is considered revocable.
Joint Tenancy: A form of co-ownership in which two or more persons hold interests in the same property with right of survivorship.
Incidents of Ownership: Rights applying to ownership interest in an insurance policy. These include the right to change a beneficiary, to borrow on a policy, to change premium modes, and so on.
Life Estate: A condition created whereby a person has the right to use property only for his or her lifetime.
Lineal Descendant: One who is, by blood relationship, in the direct line of descent from an ancestor. The term includes adopted children in Montana.
Marital Deduction (Gift): Allows married persons to make lifetime gifts to each other and claim a marital deduction for any amount without a gift tax.
Marital Deduction (Estate): Allows married persons to transform unlimited assets to the surviving spouse after the death of the first spouse without federal estate tax.
Montana Self-Sufficiency Trust: Fund that generates income to purchase supplemental services for special needs people, without jeopardizing that person’s eligibility for government benefits. Donors set up individual trust accounts that are pooled for investment purposes. Earned income is then transferred to the State Trust Fund. The State, through the Department of Health and Human Services, uses income from the MSST to purchase supplemental services designated in Lifecare Plans of trust beneficiaries.
Pay on Death (POD): Designation is the naming of a beneficiary to receive an account balance on a party’s death.
Per Capita: Equal shares to all who inherit.
Personal Representative: A person named in a will or appointed by the district court to administer the estate of a decedent. Formerly referred to as executor or administrator.
Personal Property: Assets whose ownership arises either out of physical possession of the property, or as the result of a document showing ownership. Examples: livestock, machinery, stored grain, bank deposits, stocks and bonds, checking and savings accounts, automobiles and other transportation and recreational vehicles. In Montana, all property other than real estate.
Provider Order of Life-Sustaining Treatment (POLST): Form once signed gives the patient control over medical treatments near the end-of-life.
Power of Attorney (financial): A written, notarized document in which one person gives another the power to conduct certain financial acts on his or her behalf.
Pretermitted Child: One who may, under certain circumstances, become an heir by birth or adoption subsequent to the date of execution of a testator’s will.
Private Annuity: A means of transferring property from one owner to another by “selling” it for an unsecured promise to pay the original owner an income for life of the owner or the lives of the joint owner and his/her spouse.
Probate: Process of the personal representative gathering all the property of someone who died, paying all just debts and taxes, and distributing the balance to the devisees designated in the will or to the heirs as prescribed by the legislature where there is no will or the will is defective.
Real Property: Real estate, minerals and royalty interests, growing timber, land and buildings attached to the land.
Remainderman: One entitled to the remainder of a life estate after a particular reserved right or interest has expired.
Revocable: A trust in which the trustor (maker of the trust) has, by the terms of the trust agreement, reserved the power to alter, amend or terminate the trust and to receive the property back from the trustee.
Right of Election: The surviving spouse’s right to a share of the augmented estate rather than accepting the amount provided by will or intestate succession statues. The percentage is based on the length of marriage.
Right of Representation: Describes division of property when a child receives the share of property his or her parent would have received.
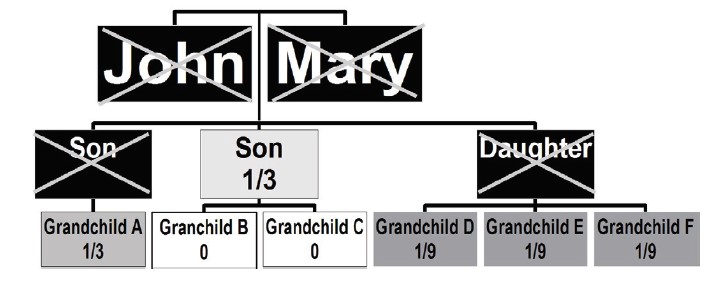
For example: John and Mary have three children who are married. Their son died 10 years ago and their daughter died 5 years ago. John and Mary died in a car accident. Grandchild A would receive 1/3 because that is the share her dad would have received if he had lived. Grandchildren D, E and F receive 1/9 each. They equally split the 1/3 their mother would have received. Grandchildren B and C receive nothing because their Dad receives 1/3.
Separate Listing of Tangible Personal Property: A list separate from the will that identifies both the items and persons to receive them.
Sole Ownership: Title to property in one name.
Spouse: A person’s wife or husband.
Succession Law: Law which governs the disposition of one’s estate if there is no will.
Tenancy in Common: A type of co-ownership between two or more persons who hold undivided interests in the same property with no right of survivorship for the surviving tenant in common. When one dies, his or her share becomes part of his or her estate. The property goes to his or her heirs and not to the other tenants in common unless they are also his/her heirs or, if there is a will, to his/ her devisees.
Testamentary: Pertaining to a will.
Testamentary Trust: A trust, set up in a will, which does not become effective until the death of the testator.
Testator: A person making a will.
Transfer on Death (TOD): Designation on securities that allows the naming of a beneficiary to receive them upon death of a party.
Transfer on Death Deed (TODD): The 2019 Montana Legislature has replaced beneficiary deeds with transfer on death deeds as a way for people to transfer their real property (located in Montana) at death to one or more beneficiaries without probate.
Trust: The legal relationship created by virtue of one party holding legal title to property, whether real or personal, for the benefit of another.
Trustee: The person, or corporate body holding title to the trust property, appointed to execute, administer, and carry out the terms of a trust for the benefit of the beneficiary.
Trustor: Maker of a trust.
Will: The legal instrument expressing a person’s wishes and directions as to the disposition and distribution of his/her property after death.
Witness: A person who observes the signing of a will and attests to the signature.

